Crypto transactions are lucrative yet risky. From private key theft to smart contract vulnerabilities, the threats in cryptocurrency trading are diverse and growing. Between 2009 and 2024, over $8.5 billion was lost due to 220 major cyberattacks. The irreversible nature of blockchain transactions, combined with unique threats like 51% attacks and insider risks, makes assessing cybersecurity critical for traders and investors.
Here’s how you can protect your assets:
- Identify threats: Focus on risks like private key theft, phishing, smart contract bugs, and counterparty fraud.
- Use tools: Employ frameworks like STRIDE, on-chain analytics, and source code audits to detect vulnerabilities.
- Analyze risks: Prioritize high-impact risks using metrics like Total Value Locked (TVL) and wallet concentration.
- Evaluate security: Vet counterparties for strong key management, and ensure protocols follow industry standards.
- Mitigate risks: Use strategies like multi-signature wallets, audits, and crypto insurance to reduce exposure.
- Monitor continuously: Leverage real-time tools like Etherscan and conduct periodic audits to stay ahead of threats.
Effective risk management combines vigilance, technical tools, and a structured approach to safeguard your cryptocurrency investments.
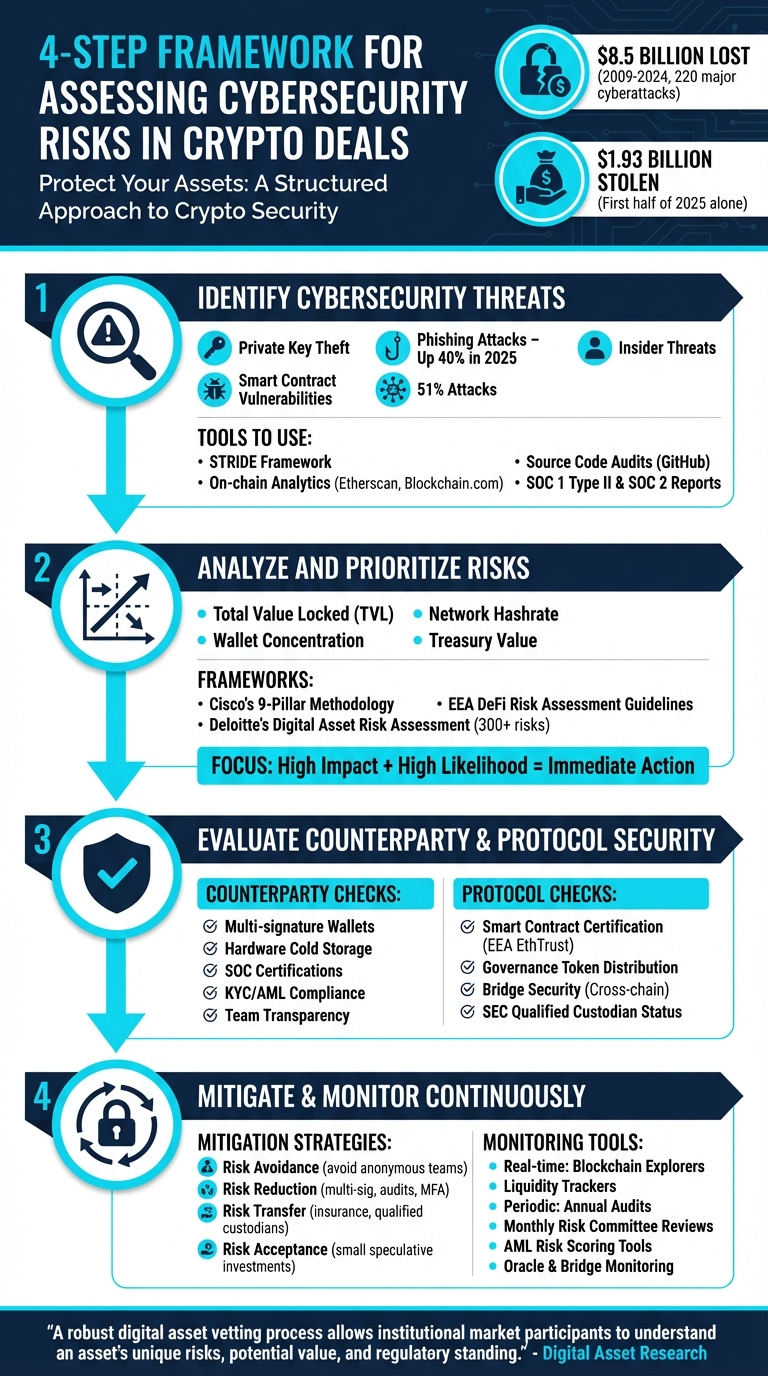
4-Step Framework for Assessing Cybersecurity Risks in Crypto Deals
Cyber risks for crypto custodians @ BAFIN

Step 1: Identify Cybersecurity Threats in Crypto Deals
The first step in safeguarding your cryptocurrency investments is identifying the threats that target these transactions. Crypto deals are particularly vulnerable to attacks stemming from both technological flaws and human errors. By understanding these risks, you can develop a strong defense strategy before committing any funds. Let’s break down the most common threats and the tools available to identify them.
Common Cyber Threats in Crypto OTC Trading
These threats pose serious risks to the security and integrity of your crypto investments.
Private key theft is one of the most devastating risks in over-the-counter (OTC) crypto trading. If hackers gain access to your private keys – whether stored on your computer or in a digital wallet – your assets can be permanently lost. Bryan Gour, Cyber Innovation Architect at City National Bank, emphasizes:
"When it comes to risks with cryptocurrency, I think the main one is that most people store their private key on their PC like any other file… once a key is stolen, there’s no getting it back."
The numbers tell a grim story: nearly $1.93 billion was stolen in the first half of 2025 through crypto-related crimes, surpassing the total for all of 2024. A significant portion of these losses came from phishing and social engineering attacks, which rose by 40% in early 2025. Fraudsters often impersonate legitimate platforms to trick users into sharing sensitive information.
Smart contract vulnerabilities are another major concern, especially in cross-chain transactions. Bugs in the code can allow attackers to reroute funds to malicious addresses. Similarly, counterparty fraud is a persistent risk in OTC trading, where trust is paramount. This includes identity fabrication, fraudulent refund claims after receiving assets, and defaults by either the counterparty or the trading facilitator. Hong Kong law enforcement estimates there are around 200 physical virtual asset OTC shops and 250 active online providers in the region, highlighting the need for thorough vetting.
51% attacks target networks with lower hashrates, enabling attackers to gain majority control of the network’s computing power and manipulate transactions. Lastly, insider threats, where individuals with privileged access exploit their position to steal assets or compromise security protocols, remain a pressing issue.
Tools for Threat Identification
Once you’ve identified potential threats, the next step is using tools to assess and monitor these risks.
A systematic approach is key to uncovering vulnerabilities. The STRIDE framework (Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, Elevation of Privilege) is a widely used method for threat modeling in crypto transactions. It helps categorize vulnerabilities across different attack surfaces.
Leverage on-chain analytics and source code audits to ensure transparency and integrity. Blockchain explorers like Etherscan allow users to verify transaction histories and monitor wallet activity. For Proof-of-Work assets, platforms like Blockchain.com help track a network’s hashrate – a declining hashrate can signal a greater risk of 51% attacks. Additionally, analyzing wallet concentration can reveal risks such as price manipulation if a small number of wallets control a significant portion of a token’s supply.
Source code auditing is another critical tool. Reviewing GitHub repositories can provide insights into a project’s activity and code quality. Dr. Giannis Tziakouris, Senior Incident Response Architect at Cisco Talos, notes:
"A regularly updated and active GitHub repository is a positive sign, indicating that the project is actively maintained and progressing towards its goals."
Conversely, inactive or closed repositories are major warning signs. For custodial services and trading platforms, requiring SOC 1 Type II and SOC 2 reports is essential. These reports independently verify a platform’s operational resilience and security controls, offering added assurance about its practices.
Step 2: Analyze and Prioritize Risks
To effectively manage risks, you need a clear understanding of their likelihood and potential impact. By focusing on high-impact risks over minor ones, you can allocate resources where they matter most.
Quantitative and Qualitative Risk Analysis
Start by assessing factors specific to crypto projects. For example, a team’s transparency plays a major role – anonymous or newly formed teams often carry a higher risk of fraud. On the other hand, active development, such as frequent GitHub commits, typically signals a more secure project. It’s also wise to look at the project’s history. Have there been past vulnerabilities or hacks? A clean track record is always a good sign.
When it comes to impact assessment, metrics like Total Value Locked (TVL), Treasury Value, and Market Cap are essential. These help quantify potential financial losses. For instance, a smart contract managing $50 million in TVL poses a much greater risk than one handling just $500,000. History has shown how a single vulnerability in a smart contract can lead to enormous losses.
Consensus mechanisms also come with their own set of risks. For Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchains, monitoring the network’s hashrate is crucial. A declining hashrate increases the chances of a 51% attack, as seen with Ethereum Classic, which suffered four such attacks between 2019 and 2020 when attackers gained control of the network’s computing power. Proof-of-Stake (PoS) systems, on the other hand, require scrutiny of wallet distribution. If a small number of wallets hold the majority of tokens, the risk of price manipulation or governance attacks becomes much higher.
Stress testing can uncover worst-case scenarios. For example, simulate a 50% asset drawdown or simultaneous defaults on major loans to identify "wrong-way risks." A striking example occurred during the stETH/ETH decoupling in June 2022, when the price ratio dropped to 0.9338 (from its usual level above 0.99), creating a liquidity crunch that led to massive liquidations for institutions using stETH as collateral. This kind of risk, where both the borrower’s ability to pay and the collateral’s value plummet simultaneously, can amplify losses significantly.
By conducting this analysis, you’ll be prepared to prioritize risks using established frameworks.
Prioritizing Risks with Frameworks
Structured frameworks help rank risks based on severity. For example, Cisco’s 9-Pillar Methodology evaluates risks across factors like Blockchain Type, Consensus Mechanism, Team, Whitepaper, Source Code, Historical Hacks, Wallet Distribution, Legal Scrutiny, and Liquidity. Generally, public blockchains are considered lower risk because of their transparency and decentralization. In contrast, private and consortium blockchains often carry higher risks due to their reliance on centralized control.
The EEA DeFi Risk Assessment Guidelines provide a targeted approach for evaluating risks related to software, governance, and oracles in DeFi protocols. For cross-chain transactions, the EEA Crosschain Security Guidelines are invaluable. They highlight the risks associated with bridges – trusted bridges introduce counterparty risk, while trustless bridges may have vulnerabilities in their code.
Another tool, Deloitte‘s Digital Asset Risk Assessment Tool, identifies over 300 blockchain-specific risks. Its waterfall approach integrates with existing controls, helping you create prioritized remediation plans tailored to your transaction context.
| Risk Factor | High Likelihood Indicators | High Impact Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Contracts | Publicly visible code with no recent audits; rushed deployment | High TVL (Total Value Locked) managed by the contract |
| Liquidity | Low trading volume; small circulating supply relative to market cap | Difficulty exiting positions; vulnerability to pump-and-dump schemes |
| Governance | Token concentration in founder wallets; lack of multi-sig protocols | Single actor’s ability to "Rug Pull" or drain the treasury |
| Oracle | Dependence on a single data source; delayed updates | Manipulated price feeds causing forced liquidations |
To visualize risks, use likelihood-impact matrices. Risks with both high likelihood and high impact should be addressed immediately, while those with low likelihood and impact can be monitored less frequently. This method ensures you focus on the most critical vulnerabilities without wasting resources on minor threats.
Once risks are analyzed and prioritized, the next step involves assessing counterparty and protocol security.
Step 3: Evaluate Counterparty and Protocol Security
Counterparty Security Assessment
When dealing with OTC crypto transactions, assessing the security of your counterparty is a critical step. Start by examining their wallet and key management practices. Look for multi-signature setups and the use of hardware-backed cold storage. Additionally, confirm whether they follow formal key ceremonies for generating or rotating cryptographic keys, as these processes ensure better security [7,15].
Operational controls are another important indicator of a counterparty’s dedication to security. Check if they enforce segregation of duties, maintain detailed and auditable logs, and comply with strict KYC/AML protocols. Validated SOC certifications, such as SOC 1 Type II for transaction processing or SOC 2 for overall security measures, can provide further assurance [7,8,15].
The team’s transparency and expertise also play a significant role. As Dr. Giannis Tziakouris, Senior Incident Response Architect at Cisco Talos, explains:
The anonymity of the development team can markedly raise the risk of monetary loss due to a lack of accountability.
A counterparty with a transparent and experienced team, coupled with a strong operational track record, poses less risk. Once you’ve verified these controls, move on to evaluating the protocol itself.
Protocol Security and Compliance
In addition to transactional risks, scrutinize the blockchain protocol for potential vulnerabilities. Ensure that the protocol’s smart contracts have been certified to meet industry standards, such as those outlined by the EEA EthTrust Security Levels. Past incidents have demonstrated why rigorous smart contract certification is essential.
Take a close look at the protocol’s governance structure. If governance tokens are heavily concentrated in a few wallets, the risk of manipulation or a "rug pull" increases significantly. Tools like Etherscan can help audit wallet distributions and assess how decentralized control truly is. For protocols involving cross-chain transactions, evaluate the security of the bridges they use. Trusted bridges may introduce counterparty risks due to centralized custody, while trustless bridges can be vulnerable to flaws in their smart contract code.
On the regulatory side, confirm that custodians meet the "Qualified Custodian" status as defined by the SEC for institutional transactions. Also, ensure compliance with guidelines from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), the SEC, and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC). Protocols should support full traceability to identify counterparties and monitor fund movements, meeting compliance requirements [7,17].
These thorough evaluations set the stage for leveraging specialized services to further mitigate risks.
Leveraging BeyondOTC‘s Networking and Services
Navigating the complexities of counterparty and protocol security can be daunting. BeyondOTC simplifies this process by utilizing its extensive network of pre-vetted trading platforms, custodians, and exchanges. Their services connect clients with trusted OTC desks, institutional investors, and liquidity providers that have already undergone stringent security evaluations, incorporating the measures discussed above.
For institutional clients handling large transactions, BeyondOTC facilitates direct access to both centralized exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) that adhere to robust security and compliance standards. This streamlined vetting process eliminates the need for time-consuming independent audits. Additionally, BeyondOTC offers legal consultancy services, linking clients with blockchain law firms to ensure counterparties meet all jurisdictional and regulatory requirements. By tapping into this curated network, you gain access to a secure ecosystem of partners while maintaining effective KYC/AML oversight throughout the transaction process.
sbb-itb-7e716c2
Step 4: Develop Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation Strategies
Risk Mitigation Techniques
Once you’ve completed a thorough risk analysis, the next step is to implement strategies that minimize potential threats in your crypto OTC trades. These strategies – risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, and risk acceptance – help you manage exposure in different trading scenarios effectively.
Risk avoidance is all about steering clear of high-risk situations altogether. For example, you might avoid projects with anonymous development teams, closed-source protocols, or private blockchains that lack transparency. While this eliminates specific risks, it can also mean bypassing early-stage opportunities with significant growth potential.
Risk reduction focuses on minimizing the likelihood or impact of potential threats through technical measures. Examples include using multi-signature hardware wallets to avoid single points of failure, setting TWAP and slippage limits to defend against sandwich attacks and front-running, and conducting thorough smart contract audits. A sobering example is the August 2021 Poly Network hack, where a bug led to $600 million in losses. Additionally, implementing MFA and wallet whitelisting adds another layer of security.
Risk transfer involves shifting financial responsibility to third parties. For instance, institutional traders can rely on "Qualified Custodians" as defined by the SEC, which offer robust security and compliance measures. Crypto insurance is another option, though it often comes with steep premiums and limited coverage. This approach is especially useful for large-value transactions, where the protection justifies the additional cost.
Risk acceptance acknowledges that some level of risk will always remain. This approach makes sense for small, speculative investments where the potential rewards outweigh the risks, or for threats inherent to the crypto space that can’t be fully eliminated. However, only accept risks where the potential upside clearly justifies the exposure.
Comparison of Mitigation Strategies
Each mitigation strategy has its strengths and weaknesses, depending on factors like transaction size, risk tolerance, and operational needs. The table below outlines these strategies, highlighting their benefits, drawbacks, and ideal use cases.
| Mitigation Technique | Pros | Cons | Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Avoidance | Completely eliminates specific risks; no implementation cost. | Potentially misses out on high-growth opportunities in emerging projects. | Best for anonymous teams, closed-source protocols, or private blockchains. |
| Risk Reduction | Strengthens security; significantly lowers the chances of hacks and exploits. | Requires technical expertise and ongoing costs (e.g., audits, monitoring). | Suitable for all OTC deals, especially those involving smart contracts. |
| Risk Transfer | Shifts financial risk to third parties; offers a safety net. | High insurance premiums; introduces reliance on custodians. | Ideal for large institutional transactions using "Qualified Custodians". |
| Risk Acceptance | Enables participation in high-reward projects with minimal upfront costs. | Exposes you to potential total loss; no fallback if risks materialize. | Appropriate for small, speculative investments. |
For high-value institutional trades, a layered approach works best. Combine risk reduction measures like multi-signature wallets and audits with risk transfer options such as custodians or insurance. For smaller, speculative trades, you might take on more risk but still apply basic protections like MFA and wallet whitelisting to minimize exposure. Tailor your strategy to fit the unique needs of each transaction.
Monitoring and Continuous Risk Assessment
Strengthening your security strategy doesn’t end with identifying threats and analyzing risks. It requires ongoing vigilance through real-time monitoring and regular audits to stay ahead of evolving dangers.
Real-time Monitoring Tools
In the world of crypto, threats don’t stay static – they’re constantly changing. That’s why real-time monitoring is a must for anyone involved in OTC trading. With the right tools, you can gain immediate on-chain and counterparty visibility, helping you act before issues spiral out of control.
Start with blockchain explorers like Etherscan and Blockchain.com. These tools give you a transparent view of transaction flows, making it easier to detect unauthorized fund movements early on. For Proof-of-Work assets, keeping an eye on the network’s hashrate is crucial. A sudden drop in hashrate could signal a looming 51% attack, as seen with Ethereum Classic in the past.
Liquidity and price trackers such as CoinMarketCap are also essential. These tools let you monitor metrics like fully diluted market caps and circulating supply, which can help you spot warning signs of pump-and-dump schemes or governance token concentration. For example, if 80% of governance tokens are controlled by just a few wallets, the risk of a rug pull becomes very real. Additionally, AML risk scoring tools are invaluable for tracking the origin and destination of crypto-assets, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
For cross-chain activities, oracle and bridge monitoring plays a critical role. Oracles must be checked for data delivery delays, while bridges – especially those holding large amounts of locked funds – are frequent hacker targets. Automated systems powered by machine learning can help identify these vulnerabilities before they lead to major losses.
This real-time vigilance lays the groundwork for the next step: periodic audits to ensure long-term security.
Periodic Audits and Updates
While real-time monitoring tackles immediate threats, periodic audits provide a deeper, long-term layer of protection. These audits validate your security measures, reconcile on-chain transactions with internal records, and keep you aligned with changing AML regulations.
"A crypto audit examines your blockchain transactions, controls, and financial records – helping you stay compliant, manage risk, and demonstrate credibility." – Javier Salinas, Partner and Blockchain & Digital Assets Leader, BPM
Set a consistent schedule for these reviews. Comprehensive audits should take place annually or at the close of the fiscal year. Additionally, a management-level risk committee should meet monthly to assess new and emerging risks. If your business is scaling quickly, launching new products, or holding over 20% of assets in non-custodial wallets, an unscheduled audit should be conducted immediately.
Don’t overlook smart contract audits – these are critical for identifying code vulnerabilities and ensuring governance mechanisms work as intended. Neglecting this step can lead to devastating consequences, like the $120 million loss from the BadgerDAO hack in 2021.
Conclusion
Managing cybersecurity risks in crypto OTC deals isn’t something you can check off a list – it’s a continuous process that requires vigilance and proactive strategies. The crypto world has seen its fair share of major security breaches, from smart contract exploits to private key thefts, making it clear that thorough due diligence is more than just a good idea – it’s a necessity.
Throughout this discussion, we’ve highlighted key steps like verifying source code integrity and implementing real-time monitoring. Together, these measures create a strong foundation for managing cyber risks in OTC crypto trading. The framework we’ve outlined – covering threat identification, risk analysis, counterparty evaluation, mitigation strategies, and ongoing monitoring – offers a structured approach to safeguarding digital assets. Whether it’s checking source code on GitHub or keeping an eye on hashrates in Proof-of-Work networks, each action addresses the unique vulnerabilities of blockchain systems, which differ greatly from traditional IT setups.
"A robust digital asset vetting process allows institutional market participants to understand an asset’s unique risks, potential value, and regulatory standing."
Tools like blockchain explorers (e.g., Etherscan) enhance transparency by providing insights into transaction flows. Additionally, risk assessment frameworks – some of which evaluate over 300 blockchain-specific risks – can help streamline your due diligence process without compromising thoroughness. These resources are crucial for assessing key factors while ensuring compliance with SEC and FATF standards.
Partnering with trusted industry players can further strengthen your security measures. For example, working with vetted services like BeyondOTC can simplify counterparty evaluations and protocol assessments. Their network connects you with established OTC desks, institutional investors, and legal advisors, helping you navigate the complex terrain of digital asset risks. In a volatile market that saw its total capitalization drop from nearly $3 trillion in late 2021 to around $1 trillion by 2023, having reliable partners who understand both the technical and regulatory sides of crypto security is not just helpful – it’s essential.
FAQs
What are the biggest cybersecurity risks in cryptocurrency deals?
Cryptocurrency transactions, particularly OTC (over-the-counter) deals, come with their fair share of cybersecurity challenges. Some of the most common threats include phishing attacks, where attackers deceive individuals into sharing confidential details, and ransomware, which locks systems until a payment is made. There’s also the risk of smart contract vulnerabilities, which can leave transactions open to exploitation. On top of that, exchange or OTC desk breaches can result in major financial losses. And let’s not overlook insider threats or supply chain attacks, where internal systems or third-party providers become the target.
To safeguard against these risks, it’s essential to perform detailed due diligence, adopt strong security protocols, and collaborate with reliable partners within the cryptocurrency space. Staying vigilant and informed can go a long way in protecting your assets from these potential dangers.
How can I assess the cybersecurity risks of a crypto counterparty?
To assess the cybersecurity risks of a crypto counterparty, start by clearly defining the focus of your evaluation. This could include their wallet infrastructure, trading platform, or the code behind their smart contracts. Pinpoint critical assets such as private key storage solutions, multi-signature wallets, and APIs. Then, identify any potential weak spots – like outdated software, insufficient access controls, or a lack of secure hardware for key storage.
Once you’ve mapped out the vulnerabilities, evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of threats like phishing attacks, insider risks, or supply-chain compromises. Rank these risks by their severity and likelihood, giving priority to the most pressing concerns. Pay particular attention to high-risk areas that could cause significant harm.
Finally, review the counterparty’s existing security measures. Look at factors like the expertise of their team, their use of multi-signature wallets, and whether they have documented governance policies or incident-response plans in place.
If you want an extra layer of assurance, consider collaborating with experts like BeyondOTC. They can help validate your findings, provide access to third-party security audits, and connect you with vetted OTC desks that adhere to strict security protocols.
How can I reduce cybersecurity risks when trading cryptocurrency?
Reducing cybersecurity risks in cryptocurrency transactions requires careful planning and proactive measures. Start by conducting thorough due diligence: assess the issuer’s technical background, verify the development team’s reputation, and ensure the protocol’s code is both open-source and thoroughly audited. To enhance security, consider using multi-signature wallets, hardware-based key storage solutions, and role-based access controls to limit exposure to vulnerabilities.
For over-the-counter (OTC) trades, prioritize working with trusted desks that enforce strict counterparty KYC checks and maintain transparent pricing practices. Strengthen your defenses by enabling multi-factor authentication, setting transaction limits, and using real-time monitoring tools to identify unusual activity. It’s also crucial to have a well-defined incident response plan in place to act quickly in the event of a breach.
If you’re looking for tailored solutions, BeyondOTC offers secure OTC trading services, connections to vetted liquidity providers, and expert governance support to help you effectively manage these risks.